
In 2023, healthcare data breaches cost the industry over $11 million per incident, highlighting the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures. The healthcare sector has increasingly become a prime target for cybercriminals due to its vast repository of sensitive data and critical operations. The digital transformation in healthcare, while enhancing patient care and operational efficiency, has also introduced new vulnerabilities. Cyberattacks on healthcare institutions have surged, with ransomware attacks being particularly prevalent. According to a report by Barracuda, healthcare accounted for a fifth of all ransomware incidents from August 2023 to July 2024. This trend underscores the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures in the healthcare sector.
Cyberattacks on healthcare facilities can have devastating operational impacts. For instance, the ransomware attack on the University of Vermont Health Network in 2020 led to a month-long disruption, affecting patient care and delaying critical treatments. Similarly, the 2021 ransomware attack on Ireland’s Health Service Executive (HSE) forced the shutdown of IT systems across the country, leading to widespread cancellations of appointments and delays in diagnostics. These incidents highlight how cyberattacks can cripple healthcare operations, leading to significant disruptions in patient care.
The financial consequences of cyberattacks on healthcare institutions are staggering. The average cost of a healthcare data breach reached $11 million in 2023, according to a report by IBM. These costs include not only the immediate expenses of mitigating the breach but also long-term costs such as regulatory fines, legal fees, and loss of patient trust. The 2024 ransomware attack on Change Healthcare, a major healthcare payment processor, is a case in point. The attack disrupted services for weeks, leading to significant financial losses and operational challenges. UnitedHealth Group, the parent company of Change Healthcare, reported that the attack cost them $872 million in the first quarter of 2024 alone. This figure includes business disruption impacts but excludes direct response costs, such as the $22 million ransom paid to the hackers. The total financial impact is projected to be between $1.35 billion and $1.6 billion for the year.
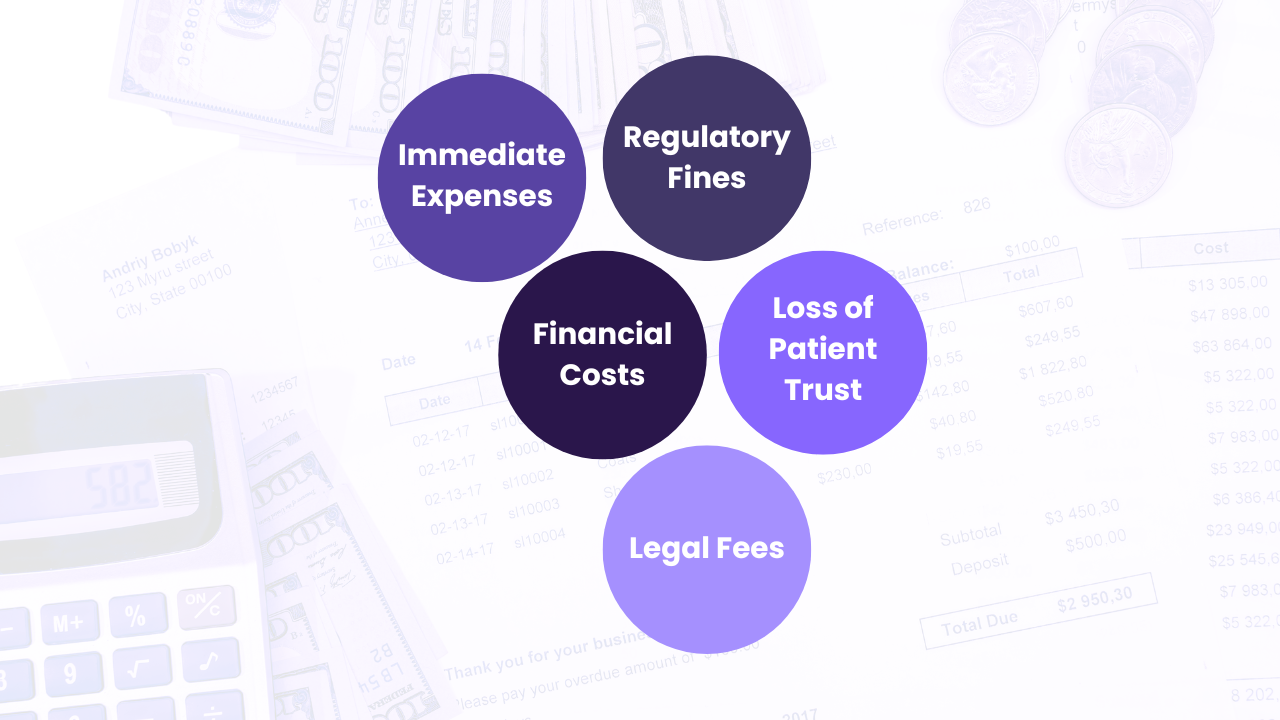
Immediate Expenses: These include costs associated with detecting and mitigating the breach, such as hiring cybersecurity experts, restoring affected systems, and notifying affected individuals. Additionally, there are costs related to downtime and lost productivity during the recovery period.
Regulatory Fines: Healthcare institutions are subject to stringent regulations, and breaches can result in hefty fines. For example, violations of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States can lead to fines ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation. Similarly, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe can impose fines up to €10 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
Legal Fees: Breaches often lead to lawsuits from affected patients, resulting in significant legal expenses. These can include costs for settlements, compensation to affected individuals, and ongoing legal representation.
Loss of Patient Trust: Data breaches can erode patient trust, leading to a loss of business and long-term reputational damage. Patients may switch to other providers, and the institution may face challenges in attracting new patients. The long-term impact on the institution’s reputation and revenue can be substantial.
Beyond financial and operational impacts, cyberattacks on healthcare institutions pose severe risks to patient safety and privacy. The 2020 ransomware attack on a hospital in Düsseldorf, Germany, resulted in the death of a patient who had to be rerouted to another hospital. In another case, a cyberattack on an Alabama hospital in 2020 led to the death of a newborn due to delayed critical tests. These incidents underscore the human cost of cyberattacks, where disruptions in healthcare services can directly impact patient outcomes and safety.
Healthcare institutions must navigate a complex regulatory landscape to ensure compliance while addressing cybersecurity threats. Regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States mandate stringent data protection measures. However, compliance alone is not sufficient. The increasing sophistication of cyber threats requires healthcare organizations to adopt proactive cybersecurity strategies. The 2024 WHO report emphasizes the need for enhanced cyber-maturity and shared cybersecurity capabilities to protect healthcare infrastructure.
HIPAA (United States): Mandates the protection of patient data through administrative, physical, and technical safeguards. Non-compliance can result in significant fines and legal consequences. For instance, breaches can lead to fines ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with a maximum annual penalty of $1.5 million.
GDPR (European Union): Requires healthcare institutions to implement robust data protection measures and report breaches within 72 hours. Non-compliance can lead to fines of up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher. This regulation emphasizes the importance of data minimization, consent, and the right to be forgotten.
NIS Directive (European Union): Aims to improve the cybersecurity of critical infrastructure, including healthcare. It requires healthcare institutions to implement appropriate security measures and report significant incidents. The directive focuses on enhancing the overall security posture and resilience of essential services.
To mitigate the impact of cyberattacks, healthcare institutions must build cyber resilience. This involves implementing robust cybersecurity frameworks, conducting regular risk assessments, and investing in advanced security technologies. Key strategies include:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data by requiring multiple forms of verification, such as passwords, biometrics, or security tokens.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Monitors and responds to threats on devices connected to the network. EDR solutions provide real-time visibility into endpoint activities, enabling rapid detection and response to potential threats.
Encryption: Protects data both in transit and at rest by converting it into a secure format that can only be accessed by authorized users. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs: Educates staff about phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics. Regular training sessions and simulated phishing exercises can help employees recognize and respond appropriately to potential threats.
Regular Risk Assessments: Conduct comprehensive risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and implement appropriate mitigation measures.
Incident Response Planning: Develop and regularly update incident response plans to ensure a swift and effective response to cyber incidents.
Collaboration and Information Sharing: Participate in information-sharing initiatives with other healthcare institutions and cybersecurity organizations to stay informed about emerging threats and best practices.
Investment in Advanced Security Technologies: Invest in technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance threat detection and response capabilities.
Studying Compliance and Regulations: Even if certain regulations are not directly applicable, studying them can provide valuable insights into best practices and help healthcare institutions implement better cybersecurity measures.
In conclusion, the healthcare sector must prioritize cybersecurity to safeguard its operations, financial stability, and patient safety. The increasing frequency and severity of cyberattacks highlights the urgent need for healthcare institutions to adopt a proactive and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. By investing in advanced security measures, fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, and ensuring regulatory compliance, healthcare organizations can enhance their resilience against cyber threats and protect the critical services they provide.
Moreover, by studying and understanding various compliance requirements, even those not directly applicable, healthcare institutions can gain valuable insights into best practices and strengthen their cybersecurity posture. This proactive approach is essential to stay ahead of evolving threats and ensure the safety and trust of patients.



