
In today's digital healthcare landscape, the security of patient data is more critical than ever. The increased reliance on electronic records and communication systems has made patient information vulnerable to various cyber threats, with phishing attacks being one of the most pervasive and dangerous.
Phishing attacks involve deceptive communications, often emails, designed to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information or installing malware. In the healthcare sector, where sensitive patient data is stored and shared electronically, phishing poses a significant threat. Understanding the anatomy of these attacks and their implications is crucial for protecting patient data.
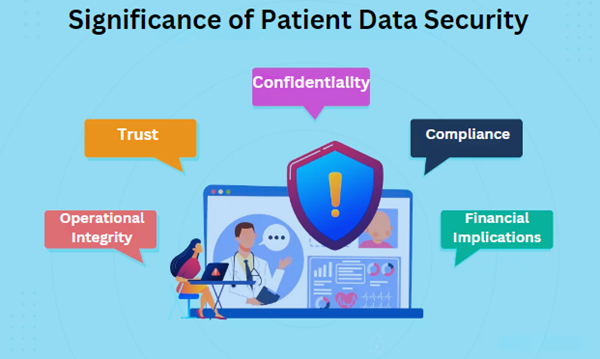
The significance of patient data security in healthcare cannot be overstated. It encompasses the protection of sensitive patient information, including personal identification, medical histories, and financial data, from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Here are key points highlighting its importance:
Confidentiality: Ensuring the privacy of patient information is a fundamental ethical obligation in healthcare. Breaches can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive medical histories and personal details.
Trust: Maintaining data security fosters trust between patients and healthcare providers, which is crucial for effective healthcare delivery.
Compliance: Healthcare organizations must comply with regulations such as the Sensitive Personal Data or Information (SPDI). IT Rules define SPDI to include information related to health, which is crucial for patient data protection.
Operational Integrity: Secure patient data is crucial for the smooth operation of healthcare services, from diagnosis and treatment to billing and administration.
Financial Implications: Data breaches can be costly, involving expenses related to breach notification, legal fees, and remediation efforts. Investing in patient data security helps prevent these costs and protects the financial stability of healthcare organizations.
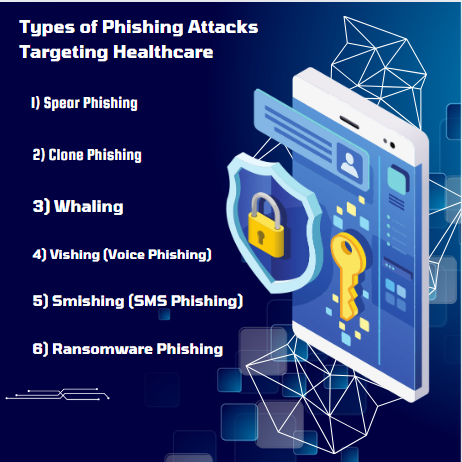
Phishing attacks targeting healthcare organizations have become increasingly sophisticated, posing significant risks to patient data and operational integrity. Healthcare entities frequently exhibit deficiencies in deploying comprehensive cybersecurity protocols, rendering them vulnerable. The accelerated digitization of electronic health records (EHRs) and the proliferation of telemedicine have expanded the attack vectors, offering cyber adversaries increased opportunities to exploit security gaps via sophisticated phishing techniques.
Spear phishing targets specific individuals within an organization, such as healthcare executives or IT personnel. Attackers often use personal details to craft convincing messages that appear legitimate.
Impact: Successful spear phishing can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive systems, financial loss, and data breaches.
Attackers create a nearly identical copy of a legitimate email previously sent by the organization, replacing attachments or links with malicious ones.
Impact: Recipients are tricked into thinking the message is a follow-up to a legitimate email, leading to malware infections or credential theft.
Target high-profile individuals such as executives within an organization, and aiming to access highly sensitive information or large financial transactions.
Impact: Compromised executive accounts can result in significant financial transfers, unauthorized access to confidential information, and overall organizational disruption.
Vishing involves attackers making phone calls pretending to be from trusted entities, such as IT support or financial departments, to extract sensitive information or credentials.
Impact: Victims may unknowingly provide login information or other sensitive data over the phone, compromising system security.
Smishing uses SMS messages to trick recipients into clicking on malicious links or providing personal information.
Impact: Clicking on malicious links can lead to malware installation on mobile devices, exposing sensitive patient data and other critical information.
Emails contain links or attachments that, when clicked or downloaded, install ransomware. This malware encrypts data and demands a ransom for its release.
Impact: Disrupts healthcare operations by encrypting critical data, demanding ransom for decryption, leading to financial losses, operational downtime, data breaches, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
The impact on patient data security is a multifaceted issue that has become increasingly significant with the advent of digital healthcare systems. As healthcare providers transition from paper-based records to electronic health records (EHRs), the potential for data breaches, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access to sensitive patient information rises. This shift has numerous implications for both patients and healthcare organizations.
Increased Risk of Data Breaches: The digitization of health records makes them more susceptible to hacking and unauthorized access. Cybercriminals target EHRs for the valuable information they contain, including personal identification details, medical histories, and financial information. Data breaches can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities that can severely impact patients' lives.
Impact on Patient Care: Secure handling of patient data directly impacts the quality of patient care. Accurate and secure data ensures that healthcare providers have reliable information to make informed decisions about patient treatment. Conversely, compromised data can lead to misdiagnoses, incorrect treatments, and other medical errors.
Operational Disruption: Operational disruption from compromised systems can impede access to Electronic Health Records (EHRs), significantly affecting patient care. Such disruptions can halt essential healthcare operations, delaying treatments and diagnoses, and reducing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of medical services, leading to potential adverse outcomes for patients.
Financial and Legal Repercussions: Healthcare organizations face significant financial and legal consequences when patient data is compromised. Costs associated with data breaches include notification expenses, legal fees, fines, and compensation for affected patients. Additionally, healthcare providers may suffer reputational damage, which can result in loss of business and trust in the community.
Compromise of Patient Confidentiality: Patient confidentiality is a cornerstone of the healthcare industry. When data security is compromised, it undermines the trust between patients and healthcare providers. Patients may become reluctant to share critical information with their doctors, potentially affecting the quality of care they receive.
In 2020, the University of Vermont (UVM) Health Network experienced a debilitating phishing attack (source: Vermont.gov). Cybercriminals sent emails to employees, masquerading as internal communications. Unsuspecting staff clicked on links in the emails, unwittingly providing attackers with network access. The attackers then deployed ransomware, encrypting patient records and disrupting hospital operations for weeks. This incident highlighted the severe impact of phishing on healthcare services and patient care.
In 2014, Health South Corporation, a major healthcare provider, suffered a significant data breach due to a phishing attack (source: in.gov). Attackers sent emails to employees, posing as executives. The emails contained links to a fake login page, where employees entered their credentials. With these credentials, attackers accessed the network and exfiltrated sensitive patient information, affecting over 6 million patients. This breach demonstrated the far-reaching consequences of successful phishing attacks.
For example: Consider the case of Nurse Ria, who worked at a bustling metropolitan hospital. One day, amidst her hectic schedule, she received an email that seemed to be from the hospital's IT department, urgently requesting her to update her system password to comply with new security protocols. The email looked legitimate, complete with the hospital's logo and IT department's signature. Trusting the source, Ria clicked the link and followed the instructions, unknowingly providing her login credentials to cybercriminals.
Within hours, the attackers used Ria’s credentials to infiltrate the hospital's network, exfiltrating sensitive patient records and deploying ransomware. Critical patient data was encrypted, and the hospital's operations were severely disrupted, affecting everything from patient care to administrative functions. Ria’s well-intentioned but misguided action demonstrates how a single phishing email can compromise an entire healthcare system, illustrating the profound impact phishing attacks can have on patient data security.

Security Awareness Training: Regular training programs can educate employees about the tactics used in phishing attacks and how to recognize suspicious emails. Simulated phishing exercises reinforce this training by providing real-world scenarios.
Advanced Email Filtering: Implementing sophisticated email filtering solutions can block phishing emails before they reach employees' inboxes. Machine learning and artificial intelligence can enhance these filters by identifying and flagging potentially malicious content.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enforcing MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code sent to a mobile device, making it more difficult for attackers to use stolen credentials.
Endpoint Protection: Deploying robust endpoint protection solutions can detect and mitigate malware delivered through phishing emails. This includes antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and advanced threat protection tools.
Incident Response Plan: A well-defined incident response plan ensures that healthcare organizations can quickly and effectively respond to phishing attacks. This plan should include procedures for isolating affected systems, notifying stakeholders, and restoring data from backups.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Conducting regular security audits and penetration tests helps identify and address vulnerabilities that could be exploited by phishing attacks, thereby reducing the risk of a successful breach.
Phishing attacks represent a significant and evolving threat to patient data security in the healthcare sector. By understanding the mechanics of these attacks and implementing robust cybersecurity measures, healthcare organizations can protect sensitive patient information and maintain the trust essential to patient care. The stakes are high, but with vigilance and proactive security practices, the healthcare industry can mitigate the risk of phishing and ensure the safety and integrity of patient data.




