
Have you ever wondered what really happens when you fall victim to a cyber attack? The dangers of malware, phishing, and ransomware are very real and can have serious consequences. From personal data theft to major business disruptions, these threats can cause a lot of damage.
In this article, we'll break down how malware, phishing, and ransomware work, and look at real examples of the harm they’ve caused. We’ll also share practical tips on how to protect yourself and your business from these dangers.
If you’re concerned about online security, whether you’re running a company or just want to stay safe, this guide will help you understand these threats and learn how to defend against them. Let’s dive into the world of cybersecurity and discover how to stay secure in today’s digital age.

Malware can infiltrate systems through various vectors, including email attachments, compromised websites, and software vulnerabilities. One of the most common vectors is drive-by downloads, where malware automatically downloads when a user visits an infected website. According to the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, 94% of malware is delivered via email.
Once inside a system, malware can steal sensitive information, disrupt operations, or install additional malicious software. The consequences can be catastrophic, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage and operational downtime. For instance, the 2017 NotPetya malware attack caused over $10 billion in damage worldwide. Efficient malware removal and malware protection are essential to mitigate such damages.
Malware comes in many forms, including viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware. Each type of malware behaves differently, from silently stealing information to locking systems and demanding ransoms. Understanding the types of malwares is crucial for developing effective malware and phishing defense strategies.

The 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack affected over 200,000 computers across 150 countries. Exploiting a vulnerability in Windows, the malware encrypted files and demanded ransom payments in Bitcoin. The attack critically disrupted healthcare services, forcing hospitals to cancel appointments and divert emergency patients. Ransomware prevention measures, such as regular software updates, could have reduced the impact of this attack.
Emotet began as a banking Trojan and evolved into one of the most destructive malware strains. It spread via phishing emails and acted as a dropper for other malware, including ransomware. By the time Emotet's infrastructure was dismantled in 2021, it had caused over $2.5 billion in damage to the financial sector.

A classic phishing attack typically involves an email that appears to come from a reputable source, such as a bank or well-known company. The email contains a link to a fraudulent website designed to steal login credentials or other sensitive information. Phishing scams often exploit human psychology, creating a sense of urgency or fear to provoke immediate action.
Phishing prevention strategies are essential for organizations of all sizes. Spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations, using detailed information to craft convincing messages. Whaling is a more targeted form of spear phishing aimed at high-level executives. These attacks can result in significant financial losses. For example, Ubiquiti Networks lost $46.7 million in a spear phishing attack in 2015.
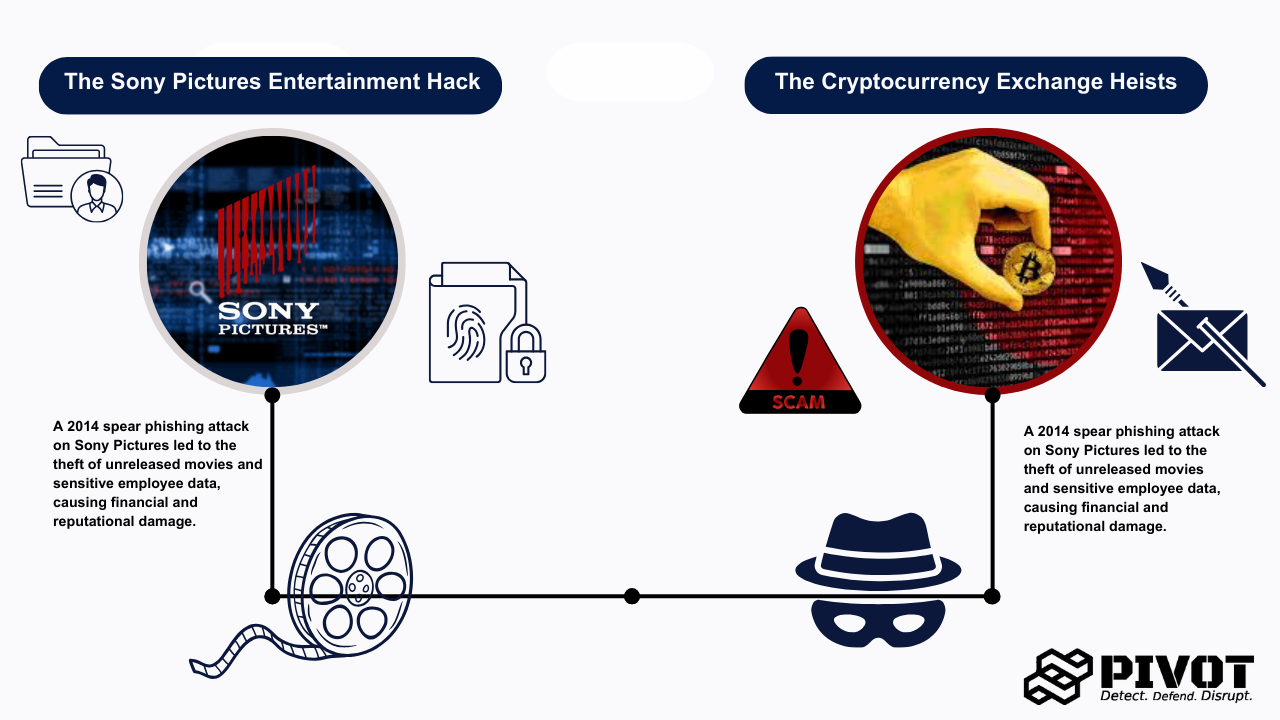
In 2014, Sony Pictures was hit by a sophisticated phishing attack that resulted in the theft of sensitive data, including unreleased movies and employee information. The attack, which targeted the company's network through spear phishing, caused extensive financial and reputational damage.
Cryptocurrency exchanges have become prime targets for phishing attacks. In 2019, Binance, one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges, was the victim of a phishing attack that led to the theft of over $40 million in Bitcoin. Attackers used phishing scams, spear phishing emails, and fake websites to compromise login credentials and bypass security measures.
RaaS has transformed the cybercrime landscape by allowing affiliates to launch ransomware attacks using pre-made tools, sharing the profits with operators. This model has led to an increase in both the frequency and scale of ransomware attacks. Cybersecurity Ventures estimates that up to 60% of ransomware attacks now occur through RaaS. Ransomware prevention and how to avoid ransomware have become critical topics for businesses and individuals.
Several ransomware variants have emerged, each with its unique strategy. Ryuk, for example, targets large organizations and demands hefty ransoms, while Sodinokibi (REvil) uses a double extortion strategy by encrypting data and threatening to release it unless paid. These ransomware solutions help organizations recover from attacks and minimize long-term damage.
In 2021, the DarkSide ransomware group attacked Colonial Pipeline, one of the largest fuel pipelines in the U.S., forcing the company to shut down its operations. The attack disrupted the fuel supply chain, highlighting the vulnerability of critical infrastructure to ransomware attacks.
The healthcare sector has become a prime target for ransomware due to the critical nature of its services. In 2020, a ransomware attack on the University of Vermont Health Network caused over $63 million in losses due to disrupted patient care.
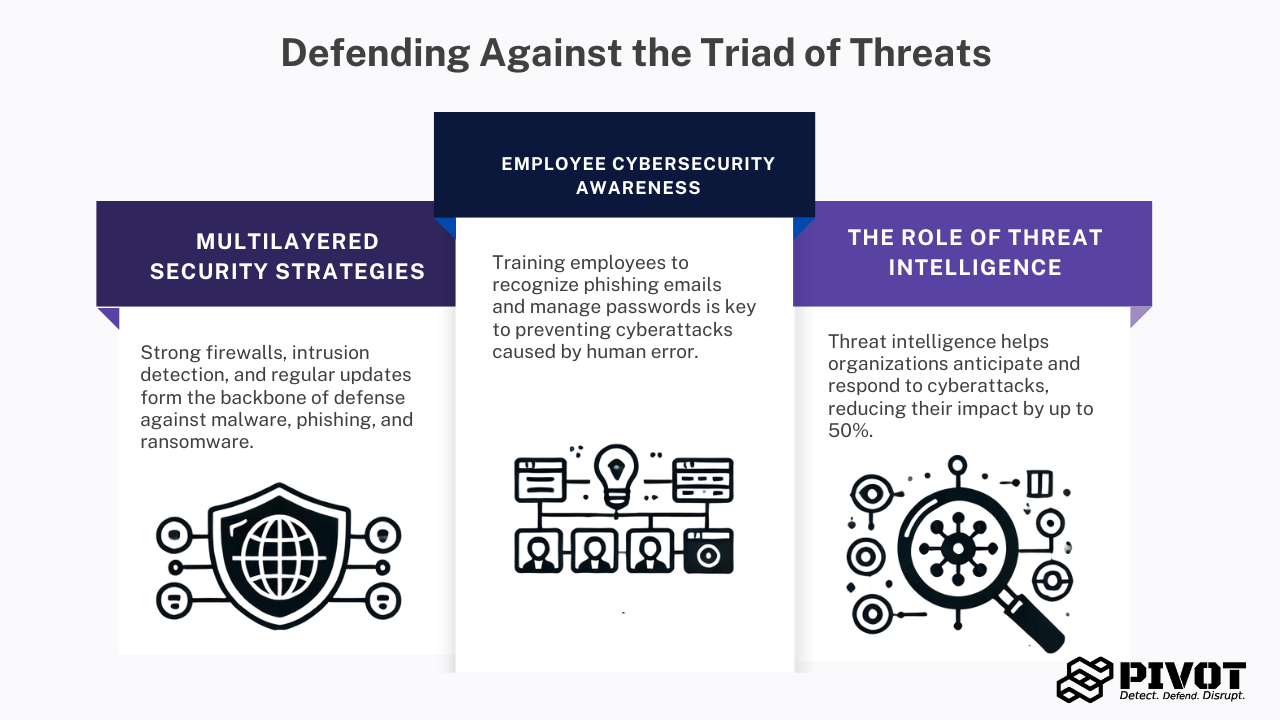
To combat malware, phishing, and ransomware, organizations must adopt a multilayered security approach. Strong firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection are crucial. Regular software updates and patch management are also vital to mitigate vulnerabilities and prevent ransomware.
Human error is a significant factor in cyberattacks. Employee cybersecurity awareness training is essential for preventing incidents. Training programs should teach employees to recognize phishing emails, avoid suspicious links, and follow best practices for password management, which plays a key role in phishing prevention.
Threat intelligence involves collecting and analyzing data on potential threats to proactively defend against cyberattacks. Organizations that leverage threat intelligence can stay ahead of emerging threats and respond to incidents more effectively. A study by the Ponemon Institute found that organizations using threat intelligence reduced the impact of cybersecurity threats by as much as 50%.
As cyber threats evolve, organizations must continuously monitor sensitive information, conduct regular security assessments, and develop proactive incident response plans to minimize risks. By understanding how to avoid ransomware and other emerging threats, companies can reduce their vulnerability to attacks.
Collaboration among organizations, government agencies, and cybersecurity experts is critical in the fight against cybersecurity threats. Sharing threat intelligence and best practices, such as through the Cyber Threat Alliance, can improve collective defense efforts.
Building cybersecurity resilience requires preparation, response, and recovery strategies, along with regular drills and ongoing development of a cybersecurity culture. A strong resilience strategy puts organizations in a better position to defend against malware, phishing, and ransomware, ensuring long-term security in the digital age.




