
As the digital landscape evolves, cybercriminals continually adapt their tactics to exploit individuals and organizations. Phishing—particularly phishing emails—is one of the most common and dangerous threats. These emails are crafted to deceive recipients into revealing sensitive information such as login credentials, financial data, or personal details, often appearing as legitimate communications from trusted sources. In this guide, we will explore practical techniques for identifying phishing emails and provide strategies to strengthen your defenses against these increasingly sophisticated attacks.
The most effective way to detect a phishing email is to closely examine the sender’s email address and domain. Attackers often practice tactics such as email spoofing to make their messages appear as though they originate from a legitimate source.
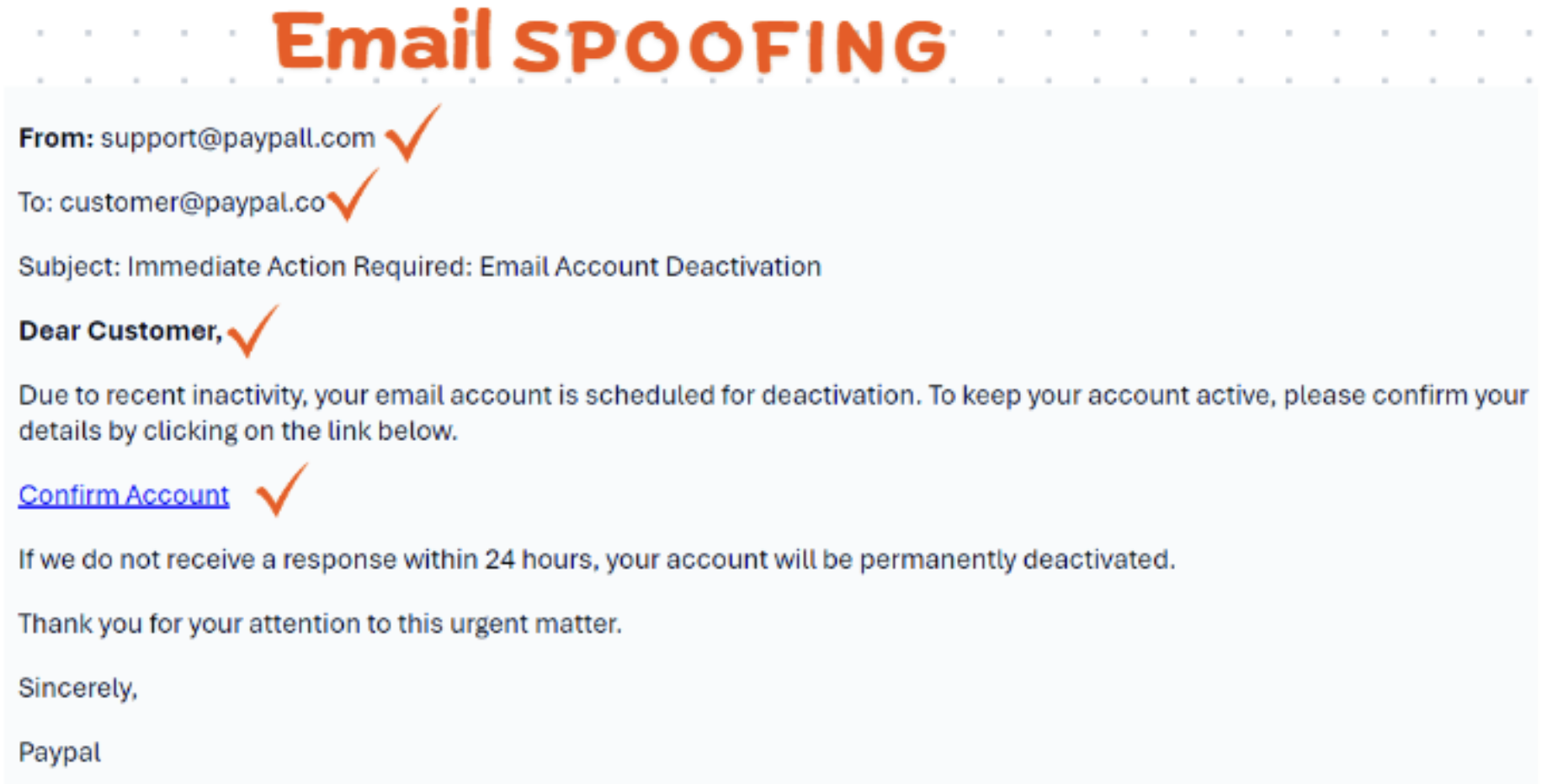
Phishers frequently use email spoofing, where they forge the sender's address to mimic a trusted entity. For example, an email might appear to come from "support@paypall.com" instead of "support@paypal.com". This subtle difference can be easily overlooked, so it's essential to verify the exact spelling of the domain.

Look for domain anomalies. Legitimate organizations usually send emails from their official domain names. Be cautious of emails from generic or free email services such as "@gmail.com" or "@yahoo.com" claiming to represent a reputable company. Furthermore, attackers sometimes use domain spoofing, where they create domains that closely resemble genuine ones like "support@paypall.com" instead of "support@paypal.com."
If you are uncertain about the legitimacy of an email, cross-check the sender’s domain with the official website of the organization. Most companies provide contact information and security tips on their websites that can help confirm the legitimacy of the communication.
Phishing emails often contain specific indicators within their content and tone that can help you identify them as malicious.
Phishers commonly use social engineering tactics to create a sense of urgency or fear. Phrases like "Your account will be suspended," "Immediate action required," or "Unauthorized login attempt detected" are designed to prompt hasty reactions. Legitimate companies typically provide reasonable time frames for you to address any issues.
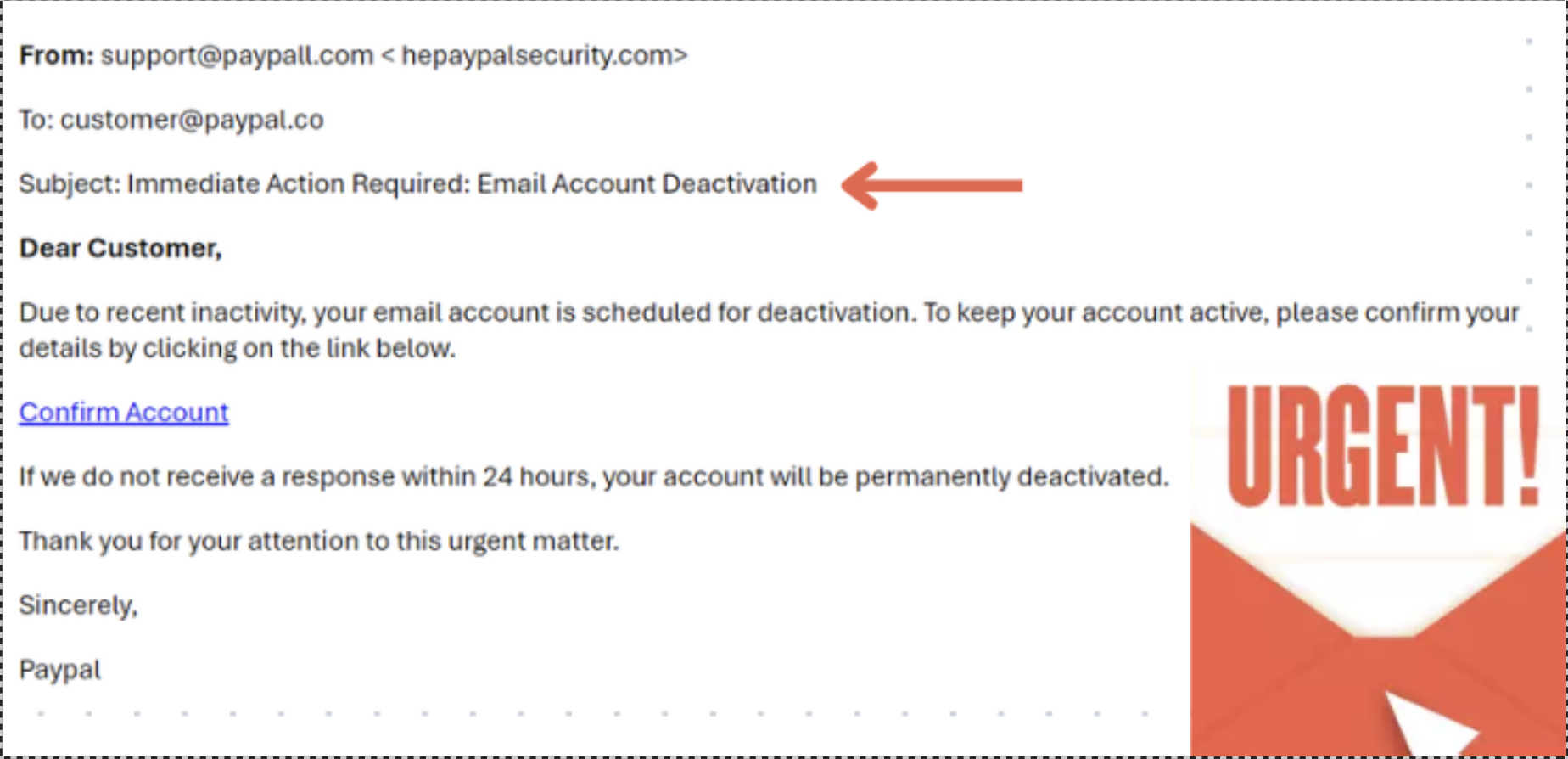
Phishing emails often start with non-personalized greetings such as "Dear Customer" or "Dear User" instead of your actual name. Authentic emails from companies you have accounts with will usually include personalized greetings.
Image Description: Example of a phishing email with generic greeting and suspicious tone.
Emails filled with spelling mistakes, grammatical errors, and bizarre phrasing can be signs of a phishing attempt. While occasional typographical errors occur, an email rife with errors is likely suspect.
Phishing emails often contain links that lead to malicious websites or attachments that install malware. Hover over any links to see the URL destination without clicking on it. If the URL looks suspicious or does not match the legitimate website, do not click. Be cautious with unexpected attachments as well.
Phishing emails often aim to steal sensitive information by masquerading as legitimate requests from trusted entities.
Legitimate companies will never ask for sensitive information such as passwords, social security numbers, or credit card details via email. If you receive an unsolicited email requesting personal information, it is almost certainly a phishing attempt.
Phishing emails may direct you to fake websites that mimic legitimate ones. Always check the URL in the browser’s address bar to ensure it begins with "https://" and has a padlock icon indicating a secure connection.
If an email raises suspicion, contact the company directly using contact information from their official website, not the details provided in the email. This step ensures you are communicating with a legitimate organization.
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are email authentication protocols used to identify and mitigate phishing emails by verifying the legitimacy of the sender's domain.
Phishing emails are a prevalent threat in the realm of cybersecurity, but by staying informed and vigilant, you can protect yourself. Always scrutinize the sender’s email address and domain, analyze the content for red flags, and verify any requests for sensitive information through official channels.
Looking to bolster your organization’s cybersecurity defenses? Get in touch with us to learn more about how we can help protect against phishing and other cyber threats.




